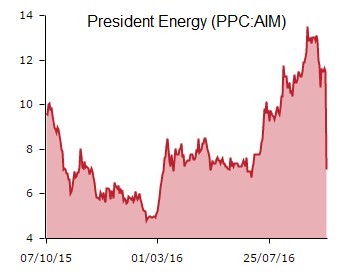
Latin American focused oil exploration and production (E&P) business President Energy (PPC:AIM) dives 36.7% to 7.28p as it is forced to suspend operations on a well aimed at doubling production from its Puesto Guardian concession in Argentina to more than 1,000 barrels of oil per day.
The news demonstrates there are risks in all forms of oil and gas drilling. This was a development well on an already discovered field, and therefore less risky than exploration drilling where a company ultimately does not know if it will be able to recover oil or not, but there are still considerable technical challenges to overcome.
Even so the litany of problems President has faced on this well are in its own words 'extremely unusual' and have occurred despite using leading contractors such as Schlumberger (SLB:NYSE) and Baker Hughes (BHI:NYSE). Issues have been encountered with the rig and the company also faced the challenge of a fractured drill pipe.
The latest problem which has led to the release of the rig to a neighbouring operator is the loss of casing (a large diameter pipe used to secure the sides of a well) down the hole. The company is considering the mobilisation of a workover rig to fish the casing out.
Executive chairman Peter Levine, who made investors a lot of money when his Russian Imperial Energy E&P venture was bought by Indian state energy company ONGC for £1.4 billion in 2011, says: 'As a first and natural step, this well will be the subject of a serious and detailed internal review as well as discussions with our service providers.
'This is not a time for kneejerk reaction and after careful assessment of the situation we will report back to shareholders.'
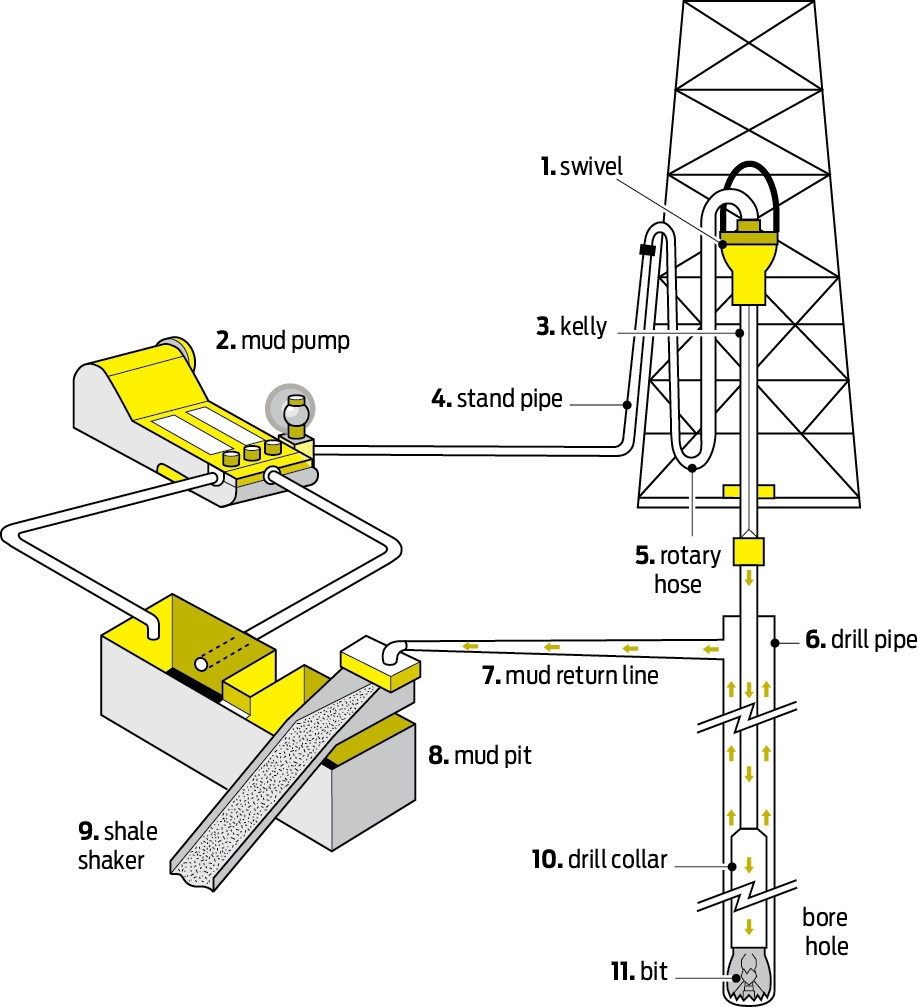
To underline the complicated process involved in drilling for oil, the diagram and key below show and describe the different elements of a basic onshore drilling rig.
Key
1. Swivel - a mechanical device that suspends the weight of the drill pipe and provides for its rotation beneath it while keeping the upper portion stationary. It also permits the flow of drilling fluids or muds
2. Mud pump - a large high-pressure pump used to circulate the mud on a drilling rig
3. Kelly - square or hexagonal-shaped steel pipe connecting the swivel to the drill pipe
4. Stand pipe - conduit for drilling mud
5. Rotary hose - a large diameter, high pressure flexible line used to connect the stand pipe to the swivel
6. Drill pipe - steel tubing used to rotate the drill bit and circulate the drilling mud
7. Mud return line - large diameter metal pipe used to direct mud from the wellbore to mud treating equipment at the surface
8. Mud pit - a large tank containing the drilling mud
9. Shale shaker - a vibrating screen that removes relatively large-sized cuttings of rock from the drilling mud returning from the well
10. Drill collar - thick-walled pipe or tube designed to provide stiffness and concentration of weight at the bit
11. Bit - The tool used to crush or cut rock
Source: E&P Forum, United Nations Environment Programme, Shares Magazine